In the current era of rapid educational transformation, digital and collaborative learning methods are reshaping how higher education institutions approach teaching and assessment. Collaborative learning, in particular, stands out as a vital approach for boosting academic performance and nurturing essential soft skills like creativity, adaptability, and emotional intelligence. By encouraging interaction, shared problem-solving, and group accountability, collaborative learning equips students to tackle the complexities of the modern workforce.
As universities across the globe embrace new technologies, the integration of AI-powered tools and collaborative platforms is revolutionizing the student learning experience. These innovations allow educators to develop courses to individual needs, streamline workloads, and build a more inclusive and adaptable learning environment. The emphasis on collaboration aligns with the rising demand for teamwork and collective problem-solving skills, which are highly valued by employers.
What is Collaborative Learning?
Collaborative learning is an educational approach where students work together in groups, sharing the responsibility for learning and collectively engaging in tasks, projects, or problem-solving activities. This method emphasizes the importance of group dynamics and the synergy that arises when individuals combine their unique skills and perspectives to achieve a common goal. Unlike self-paced learning, where individuals learn independently, collaborative learning creates a sense of community and mutual accountability, encouraging students to teach and learn from one another.
In this collaborative environment, students contribute to a shared objective by tackling specific aspects of a task while simultaneously developing their own skills. The interaction within groups not only enhances academic understanding but also nurtures critical interpersonal skills such as communication, problem-solving, and teamwork. Collaborative learning, therefore, extends beyond the classroom, preparing students for professional settings where collaboration is essential. Moreover, in online learning environments, this approach can help alleviate feelings of isolation by promoting connections among students, thereby creating a more engaging and supportive educational experience.
Why Collaborative Learning Matters?
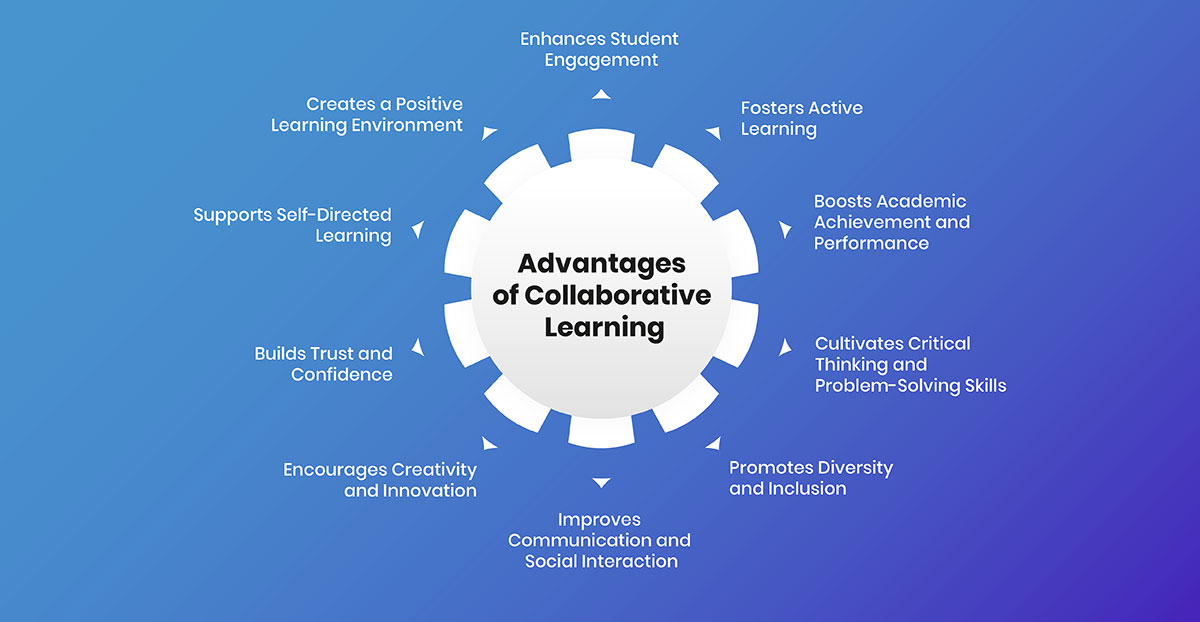
Collaborative learning is more than just group work; It's a dynamic educational method that prompts students to interact, exchange diverse viewpoints, and build essential problem-solving abilities. Let's delve into the various advantages of collaborative learning.
-
1. Enhances Student Engagement
Collaborative learning creates opportunities for students to connect, communicate, and engage in various virtual and in-person group activities. Through tools like video conferencing, students can participate in group projects, study sessions, and discussions, enhancing their engagement both inside and outside the classroom. -
2. Fosters Active Learning
Active learning spaces are essential for encouraging students to question, explore, and interact with their peers. Collaborative technologies, such as digital whiteboards and interactive sessions, support active learning, making it easier for students to remain engaged and motivated in both remote and in-person settings. -
3. Boosts Academic Achievement and Performance
Research has shown a strong link between collaborative learning and improved academic outcomes. By working in groups, students are more likely to develop a deeper understanding of the material, exhibit greater persistence, and achieve higher levels of performance. -
4. Cultivates Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills
Collaborative learning encourages students to think critically and solve problems through group discussions and peer review. This process not only enhances their problem-solving abilities but also inculcates higher-order thinking skills that are crucial for success in academic and professional settings. -
5. Promotes Diversity and Inclusion
Working in diverse groups allows students to gain exposure to different perspectives and ideas, enriching their learning experience. It builds open-mindedness and helps students appreciate the value of diverse viewpoints, which is essential in today’s globalized world. -
6. Improves Communication and Social Interaction
Effective communication is at the heart of collaborative learning. By engaging in group activities, students practice and improve their verbal and written communication skills, as well as their ability to listen actively and respond thoughtfully. -
7. Encourages Creativity and Innovation
The combination of different viewpoints in collaborative settings often leads to creative solutions and innovative ideas. This dynamic environment nurtures creativity by allowing students to build on each other's ideas and explore new approaches to problem-solving. -
8. Builds Trust and Confidence
Collaborative learning requires students to trust their peers and work together toward common goals. This trust-building process enhances their confidence, making them more willing to share their ideas and take on leadership roles within the group. -
9. Supports Self-Directed Learning
In collaborative learning environments, students take greater responsibility for their learning. They have the autonomy to explore topics at their own pace, using tools that allow them to review, pause, and reflect on their progress. -
10. Creates a Positive Learning Environment
Collaborative learning gives a supportive and constructive atmosphere where students feel valued and recognized for their contributions. This positive environment enhances their self-esteem, reduces anxiety, and promotes a more enjoyable learning experience.
Key Collaborative Learning Strategies
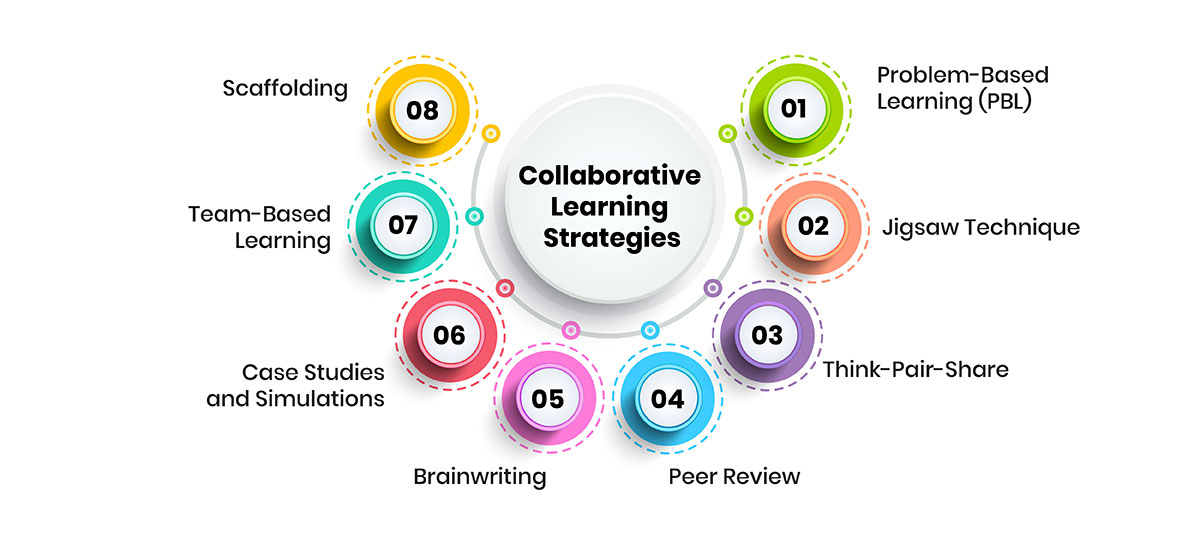
Collaborative learning in traditional and online classrooms offers numerous methods to engage students, enhance their understanding, and develop essential skills. Below, we'll explore several effective collaborative learning strategies.
-
1. Problem-Based Learning (PBL)
In PBL, students collaborate in groups to tackle complex problems, often requiring extended effort and the production of deliverables. This method emphasizes the application of knowledge and critical thinking, as students engage in research, problem-solving, and project development. It also fosters teamwork as students must rely on each other's strengths to reach a solution. -
2. Jigsaw Technique
The Jigsaw Technique divides a larger problem or topic into smaller, more manageable parts. Each student or group becomes an expert on one part and then shares their findings with the class. This method not only enhances understanding by breaking down information but also promotes interdependence, as each student’s contribution is essential to complete the "puzzle." -
3. Think-Pair-Share
Think-Pair-Share encourages individual reflection followed by peer discussion. Initially, students think independently about a question or problem, then discuss their thoughts with a partner. Finally, pairs share their insights with the larger group. This approach promotes critical thinking and ensures that all students actively participate in the learning process. -
4. Peer Review
Peer Review involves students evaluating each other's work, providing constructive feedback aimed at improving the quality of assignments. This strategy enhances analytical skills, teaches students to communicate feedback effectively, and encourages reflective learning as students apply the feedback to their work. -
5. Brainwriting
Brainwriting is a brainstorming technique where students first generate ideas individually and anonymously before sharing them with the group. This method allows for more creative and diverse contributions, as students are not influenced by others' ideas and can express themselves freely. It ensures equal participation and often leads to more innovative solutions. -
6. Case Studies and Simulations
In this approach, students engage with real-world scenarios to apply theoretical knowledge in practical situations. Case studies require students to analyze and solve specific problems, while simulations involve role-playing to experience and address challenges in a controlled environment. Both methods are effective in developing problem-solving skills and understanding complex concepts. -
7. Team-Based Learning
Team-Based Learning involves students working in teams to engage with study materials through interactive activities. After individual preparation, students collaborate on quizzes, projects, and discussions to deepen their understanding and apply knowledge in practical tasks. This approach enhances teamwork, sharpens analytical thinking, and strengthens group collaboration skills. -
8. Scaffolding
Scaffolding provides structured support to students as they develop the skills needed for independent learning. Initially, instructors offer guidance through examples and community guidelines, gradually reducing support as students gain confidence and competence. This strategy is crucial for building a strong foundation for collaborative work and ensuring student success in more complex tasks.
Implementing Collaborative Learning
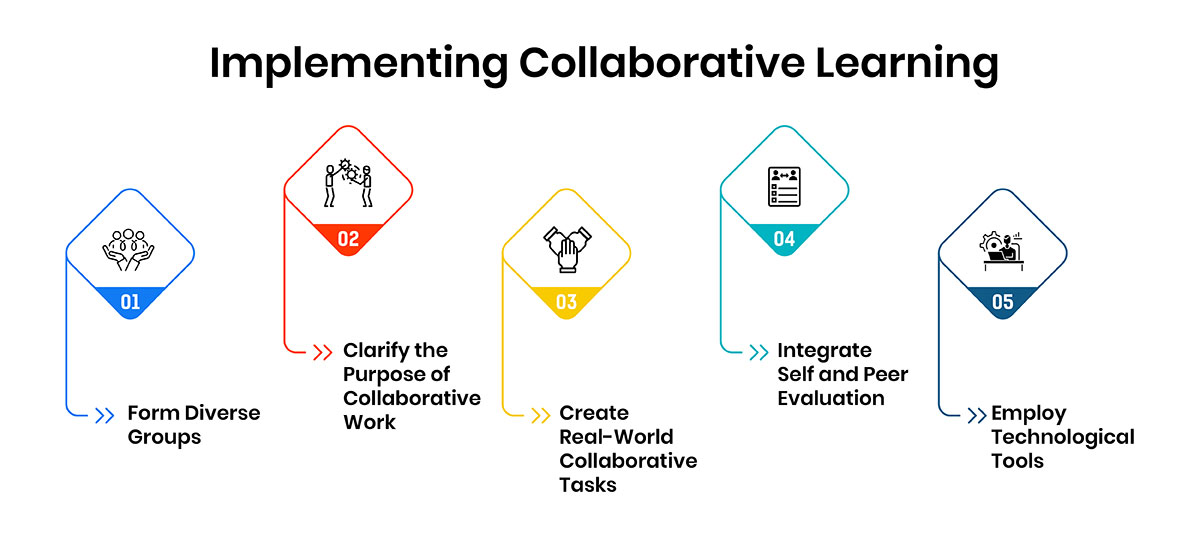
Implementing collaborative learning involves creating environments where students actively engage with peers to achieve shared goals. By strategically designing group activities, educators can make learning more dynamic and effective.
-
1. Form Diverse Groups
To optimize collaborative learning, carefully consider how you group students. Avoid allowing students to self-select groups, as this may lead to homogeneity and exclusion. Instead, create diverse groups with varying skills, backgrounds, and social dynamics to foster richer interactions and perspectives. Use surveys to gather insights about students' backgrounds to ensure balanced and effective group composition, ideally with four to five members per group. -
2. Clarify the Purpose of Collaborative Work
Ensure students understand the value of working together by providing clear, detailed instructions and explaining how these activities contribute to their learning goals and real-world skills. Set explicit guidelines for effective collaboration, including how to express opinions, provide and receive feedback, and handle non-contributing members. Engaging students in crafting these guidelines can enhance their commitment and clarity. -
3. Create Real-World Collaborative Tasks
Design activities that simulate real-world challenges to develop key skills like teamwork and problem-solving. The few strategies that we mentioned earlier can be used wisely and effectively according to the needs of the classroom and the changes to be brought about in student learning. By engaging in authentic scenarios, students develop skills that are directly applicable to professional environments, making their learning experience more relevant and impactful. -
4. Integrate Self and Peer Evaluation
Cultivate a sense of responsibility by having students assess both their own and their peers' contributions. Develop a comprehensive rubric to guide these evaluations, ensuring clarity on expectations and encouraging accountability. -
5. Employ Technological Tools
Utilize technology to streamline and support collaborative activities. Tools can assist in forming groups, managing feedback, and facilitating discussions. Numerous platforms offer solutions for efficient group work management, feedback integration, and engagement, helping to enhance the overall learning experience.
Conclusion
Integrating collaborative learning into higher education represents a transformative shift towards a more engaging and student-centered educational experience. This approach not only enhances student interaction and problem-solving but also cultivates essential skills such as teamwork and adaptability. By building a collaborative environment, institutions can offer more dynamic and effective learning opportunities that align with the demands of today's interconnected and evolving professional landscape. Embracing this paradigm not only enriches the academic journey but also prepares students to excel in both their future careers and in a rapidly changing world.
Latest
Trends blogs
- Mid-Career Education in a Changing Labor Market
- The Next Phase of STEM Education: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Classroom Curricula
- Education Technology in 2026: Trends Driving the Next Wave of Learning
- Aligning Education with Employability: The Rise of Skill-Centered Learning
Focus blogs
- Research-Driven Education: Strengthening Strategies, Policies, and Classroom Practice
- Professional Certifications for Career Growth: What Students and Young Professionals Need to Know
- Building a High-Impact Center of Excellence: What You Need to Know
- Beyond Graduation: The Importance of Lifelong Learning in Higher Education





