Building Future-Ready Students: The Essential Role of Educational Institutions
August 06, 2024In an era marked by technological breakthroughs and evolving job markets, the role of educational institutions in readying students for future careers is more csritical than ever. As leaders in higher education, it is essential to anticipate these changes and proactively address the evolving landscape of employment. Institutions can achieve this by implementing structured strategies that align with industry demands, ensuring students are well-equipped to thrive in a dynamic and tech-centric world.
The rapid adoption of advanced technologies by businesses worldwide is transforming job roles and creating new career opportunities, necessitating a workforce adept in relevant skills. The growing demand for tech-savvy professionals underscores the need for educational institutions to develop curricula that bridge current gaps and anticipate future needs. Emphasizing lifelong learning and adaptability over immediate post-graduation employment prepares students for sustained success in an ever-changing job market. By building these attributes, educational institutions can help students navigate and excel in the global talent pool, ensuring their readiness for the challenges and opportunities of the future.
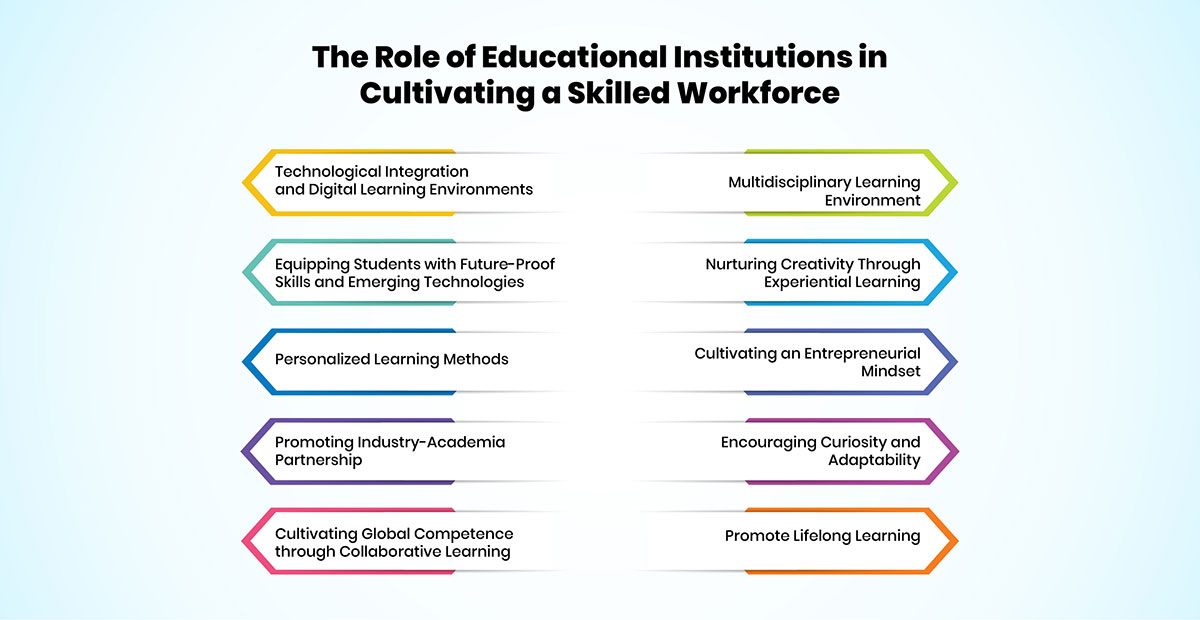
The Role of Educational Institutions in Cultivating a Skilled Workforce
Educational institutes play a crucial role in equipping students with the essential skills and competencies needed for a dynamic and evolving workforce.
-
Technological Integration and Digital Learning Environments
Seamlessly integrating technology into the learning environment is crucial for educational institutions to remain competitive. By fostering digital learning environments, universities can offer immersive and interactive experiences that traditional classrooms cannot. Technologies like VR can simulate real-life scenarios, providing hands-on experience and enhancing the learning process.Offering courses on emerging technologies and collaborating with industry partners ensures that students are comfortable and confident with new tools. Accessibility to a wide range of courses and multimedia resources further enriches the educational experience, making it more engaging and effective.
-
Equipping Students with Future-Proof Skills and Emerging Technologies
Educational institutions must prioritize developing skills that are less likely to be automated, such as critical thinking, creativity, and emotional intelligence. Integrating these competencies into the curriculum through interactive and experiential learning methods is essential. Additionally, institutions should offer courses on emerging technologies like AI, ML, and data analytics to ensure students are well-prepared for future technological advancements and remain competitive in the job market. -
Personalized Learning Methods
A one-size-fits-all approach to education is outdated. Personalized learning caters to individual preferences and needs, allowing students to learn at their own pace. Customizing courses and offering flexible modules help students identify and strengthen their weak areas, leading to better outcomes. -
Promoting Industry-Academia Partnership
Collaborations between educational institutions and industries ensure that students acquire relevant skills. These partnerships provide insights into industry trends and create opportunities for internships and practical experience. Aligning academic programs with industry needs fosters innovation and prepares students for real-world challenges. -
Cultivating Global Competence through Collaborative Learning
Students must possess a global mindset and cross-cultural competence, which can be developed through international exchange programs and multicultural experiences on campus. Additionally, fostering collaborative learning environments mirrors the nature of modern workplaces, enhancing communication, teamwork, and leadership skills. Together, these approaches help students adapt to diverse settings and cultivate a sense of community, making them highly valuable in the global job market. -
Multidisciplinary Learning Environment
Encouraging students to draw on diverse perspectives from different fields is essential for solving complex global issues. A multidisciplinary approach develops creativity and adaptability, equipping students with the skills needed to thrive in a dynamic job market. -
Nurturing Creativity Through Experiential Learning
Memorizing facts is no longer sufficient for success in today's world. Creativity is crucial, and students should be encouraged to think outside the box. By valuing and rewarding creative efforts and removing constraints, educators can cultivate a classroom environment where creativity thrives.Learning by doing enhances practical skills and real-world understanding. Incorporating internships, project-based assignments, and simulations into the curriculum bridges the gap between academia and industry. This combined approach not only nurtures creativity but also develops critical thinking, problem-solving, and adaptability, preparing students to handle complex problems in innovative ways, a skill highly valued in the modern workplace.
-
Cultivating an Entrepreneurial Mindset
Encouraging innovation and entrepreneurship prepares students for the future job market. Offering entrepreneurship courses and establishing incubation centers can nurture an entrepreneurial spirit. Normalizing failures and appreciating efforts increase students' risk appetite and resilience. -
Encouraging Curiosity and Adaptability
Curiosity is a critical driver of learning and innovation. While it isn't inherently a trait one can develop, educators can create environments that stimulate curiosity through engaging and varied activities. Extracurricular programs can break the monotony of academic routines, activating different areas of the brain and nurturing a deep, rational thought process.Additionally, change is a constant in today's fast-paced world. Teaching students to embrace change rather than fear it is vital for their success. Flexibility and adaptability are crucial skills that can help students thrive in unpredictable environments. Encouraging curiosity, a growth mindset, and resilience can help students navigate the uncertainties of the future job market, leading to better relationships and deeper engagement with content.
-
Promote Lifelong Learning
A culture of lifelong learning is essential in a rapidly evolving job landscape. Offering professional development programs and access to digital resources encourages continuous upskilling. Promoting a growth mindset and curiosity ensures students remain adaptable and competitive.
Employability: Closing the Skills Gap
To succeed in the modern labor market, students must develop a well-rounded and adaptable skill set, which includes:
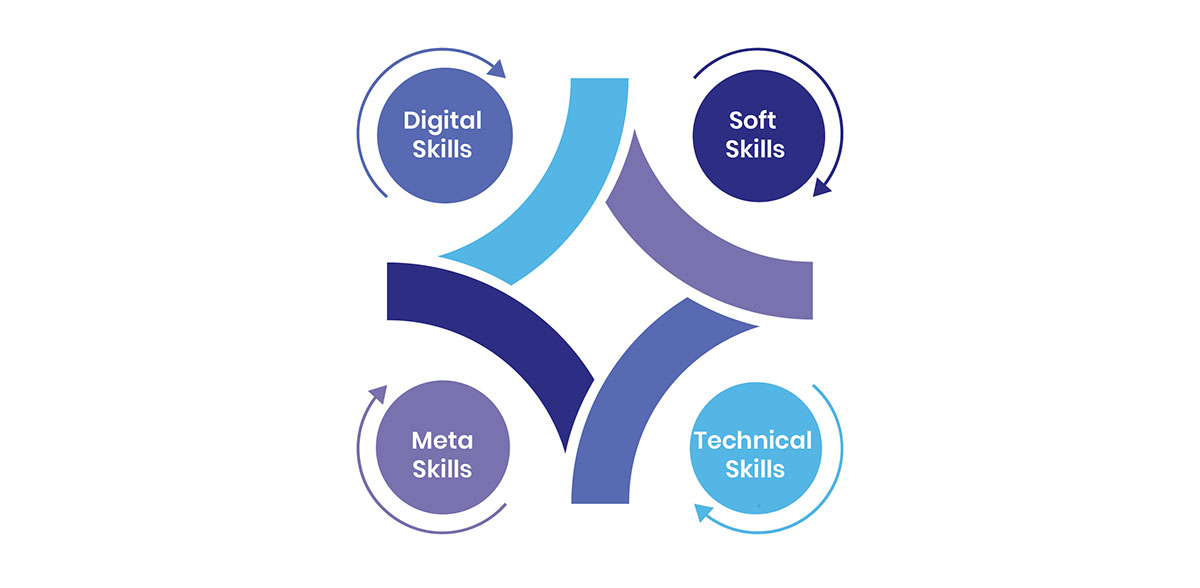
- Digital Skills: Proficiency in technologies like AI, ML, cloud computing, and big data.
- Soft Skills: Attributes such as active learning, resilience, stress tolerance, and flexibility.
- Meta Skills: Cognitive skills like problem-solving, critical thinking, and creativity.
- Technical Skills: Role-specific competencies for competitive differentiation.
A focus on employability over mere employment ensures students are prepared for lifelong success.
Considerations for Universities in Building Employability
To enhance employability, universities may focus on several key areas:

1. Curriculum Design
- Industry-Relevant Courses: Align the curriculum with industry standards and job market trends, involving updates and collaborations with industry experts.
- Soft Skills Training: Integrate communication, teamwork, problem-solving, and critical thinking into the curriculum.
- Interdisciplinary Learning: Encourage courses across different disciplines to broaden students' skill sets.
2. Practical Experience
- Internships and Work Placements: Provide hands-on experience through internships, co-op programs, and work placements.
- Real-World Projects: Incorporate project-based learning and real-world case studies.
- Industry Partnerships: Develop partnerships with businesses for mentorship, internships, and job placements.
3. Career Services
- Career Counseling: Offer guidance to help students identify strengths and career paths.
- Resume and Interview Preparation: Provide workshops on resume writing, cover letters, and interview techniques.
- Job Search Assistance: Maintain a job portal and support job searches through networking opportunities and job fairs.
4. Skills Development
- Technical Skills Training: Ensure proficiency in field-specific technical skills.
- Digital Literacy: Emphasize digital skills and provide relevant training.
- Lifelong Learning: Promote continuous learning and professional development.
5. Networking Opportunities
- Alumni Networks: Use alumni networks for mentorship, networking, and job opportunities.
- Industry Events: Host panels, guest lectures, and networking events.
- Professional Associations: Encourage joining professional associations and attending conferences.
6. Support Services
- Mental Health and Well-being: Provide services to support mental health and well-being.
- Financial Aid and Scholarships: Offer financial support to ensure educational access.
- Inclusive Environment: Promote diversity, equity, and inclusion.
7. Feedback and Improvement
- Employer Feedback: Seek feedback from employers on graduate performance and curriculum relevance.
- Student Feedback: Act on feedback from students about learning experiences and career services.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly assess and improve programs, services, and partnerships.
Conclusion
The evolving landscape of employment demands that educational institutions play a pivotal role in preparing students for future challenges. By focusing on aligning curricula with industry needs and nurturing a culture of lifelong learning and adaptability, universities can effectively bridge the skills gap. Emphasizing soft skills alongside technical proficiency and promoting diverse learning opportunities ensures graduates are not just job-ready but equipped to thrive in dynamic and competitive global markets. Through continuous improvement and robust partnerships, universities can empower students to embark on successful and fulfilling careers, poised to contribute meaningfully to the ever-changing world around them.




