Experiential Learning: Transforming STEM Education
February 07, 2025In the dynamic world of Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM), engaging students effectively is a challenge that requires innovative approaches. Hands-on, experiential learning has emerged as a transformative strategy, offering students active engagement with real-world concepts and applications.
STEM subjects can be daunting for many, and gaps in STEM literacy often lead to long-term academic and career challenges. By adopting experiential learning methods, educators create an environment where students actively participate, apply theoretical knowledge, and develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This approach not only enhances understanding but also inspires enthusiasm and confidence in STEM fields.
Experiential Learning: What It Means and Why It Matters
Experiential learning is an active, immersive educational approach that emphasizes learning through direct experience. Unlike traditional methods that rely heavily on lectures and textbooks, this approach encourages students to engage, explore, and experiment in real-world scenarios, creating deeper comprehension and retention of complex concepts.
At its core, experiential learning revolves around "learning by doing," empowering students to connect theoretical knowledge with practical applications. This methodology allows learners to tackle challenges, pose questions, and solve problems while cultivating creativity and critical thinking. It shifts the focus from passive absorption of information to active participation, where students take responsibility for their learning journey.
In STEM education, experiential learning proves particularly impactful. By engaging students in hands-on projects and real-life applications, it helps demystify challenging concepts, build problem-solving skills, and ignite curiosity. Experiential learning also supports and incorporates key educational standards, encouraging inquiry-based activities that develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Programs that offer dedicated STEM labs provide opportunities for students to experiment and work on real-world problems, preparing them for future academic and career success. Through this student-centered approach, educators can create dynamic learning environments that not only enhance academic outcomes but also prepare learners for real-world challenges.
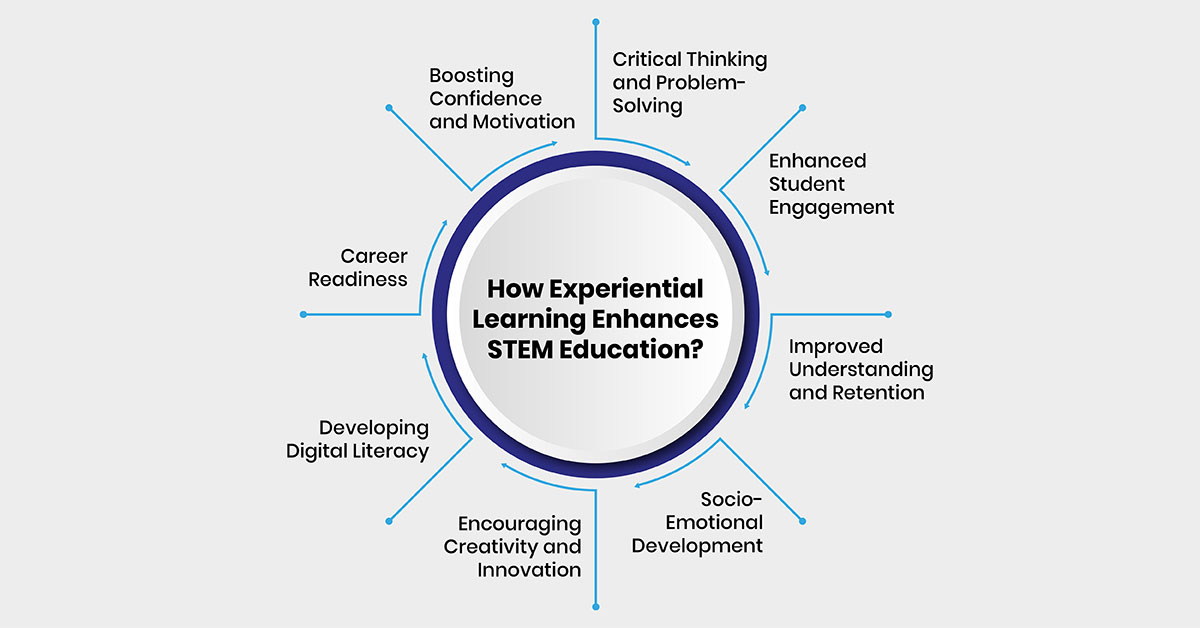
How Experiential Learning Enhances STEM Education?
Experiential learning improves education by linking classroom concepts to real-life experiences. It helps students understand better, think critically, and gain valuable skills. Let us look into a few of the benefits of experiential learning in STEM education:
-
Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving
Experiential learning encourage students to actively analyze, question, and apply STEM concepts in real-life scenarios. This immersive process nurtures critical thinking, enabling learners to identify problems, explore potential solutions, and make well-informed decisions. -
Enhanced Student Engagement
Real-world applications of STEM concepts make learning more relatable and exciting. Students become actively involved, as they see how abstract theories translate into practical solutions, sparking their interest and motivation to delve deeper into STEM fields. -
Improved Understanding and Retention
Hands-on experiences help students better grasp and retain STEM concepts by linking them to real-world contexts. Practical applications, such as solving everyday problems or building projects, allow learners to see the relevance of their education, leading to long-term retention and deeper comprehension. -
Socio-Emotional Development
By working collaboratively on experiential projects, students develop essential communication, teamwork, and interpersonal skills. Group activities teach them to listen, compromise, and consider diverse perspectives, which are crucial both in academic settings and future professional environments. -
Encouraging Creativity and Innovation
Experiential learning stimulates innovative thinking by challenging students to explore unconventional ideas and develop multiple solutions. This approach equips learners to adapt to the rapid technological changes in STEM industries while fostering originality and adaptability. -
Developing Digital Literacy
Practical exposure to technology enhances students’ ability to use, troubleshoot, and adapt to digital tools. These skills not only support academic success but also prepare them for technology-driven workplaces. -
Career Readiness
Experiential learning bridges the gap between classroom education and professional expectations. By engaging in activities that mirror real-world STEM careers, students gain insight into potential job roles, helping them make informed decisions about their career paths. -
Boosting Confidence and Motivation
Hands-on learning empowers students to take ownership of their education. Overcoming challenges and learning from mistakes in a supportive environment helps build confidence and a growth-oriented mindset, making students resilient and motivated in their academic journey.
Implementing Experiential Learning in the Classroom
The concept of experiential learning, though rooted in ancient philosophical inquiry, was formalized in the 1980s by David Kolb. Kolb’s model outlines a four-step process that guides learners from real experience to reflection, conceptualization, and ultimately active application. This cyclical process not only reinforces understanding but also encourages deeper engagement with the material.
The process of experiential learning would be:
- 1.Concrete Experience: Actively engage in the learning activity or experience.
- 2. Reflective Observation: Step back and reflect on the experience, noting thoughts and feelings.
- 3. Abstract Conceptualization: Analyze reflections to develop conclusions or new concepts.
- 4. Active Experimentation: Apply the newly acquired knowledge in real-world scenarios or problems.
Through this process, experiential learning builds a deeper connection with the material. It allows learners to not only grasp theoretical concepts but also actively engage in problem-solving, making the learning process both meaningful and practical. Educators can maximize this effectiveness by aligning these operational activities with real-life contexts, ensuring that students are able to connect classroom learning with practical applications.
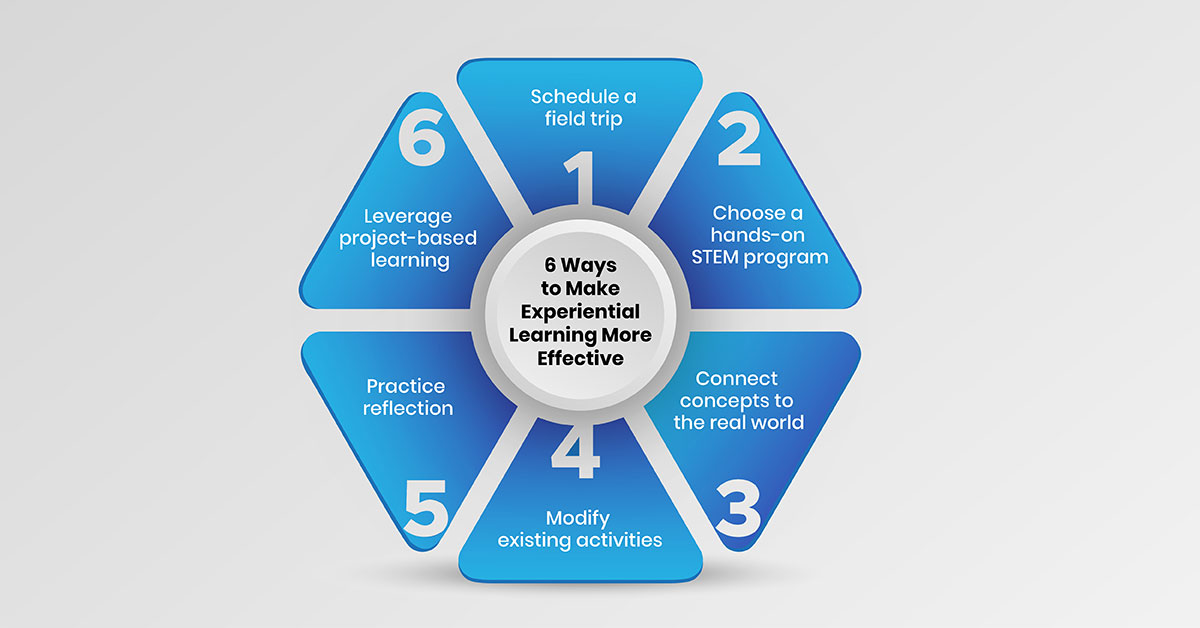
Ways to Make Experiential Learning More Effective
There are a few steps you can take to successfully bring in experiential learning and ensure its effectiveness:
-
1.Schedule a Field Trip
There are countless opportunities to take your students out into the world to show them applications of STEM, and these field trips make for great experiential learning projects. Look beyond traditional museums where students may just absorb information visually, and instead pursue those trips that let students explore real-world STEM and get demonstrative experience. -
2.Choose a Hands-on STEM Program
A great STEM program can be the cornerstone of experiential learning in STEM classrooms in elementary school, middle school, and beyond. Look for exclusive programs which features a comprehensive educational standards aligned curriculum and professional development tools, making the integration of STEM into your classroom seamless. These advanced STEM programs utilize durable engineering materials for hands-on activities that encourage critical thinking and creativity. -
3.Connect Concepts to the Real World
Many STEM subjects can seem abstract and difficult for students to engage with beyond a superficial level. Don’t be afraid to bring in news stories and practical applications of what you’ve been teaching, encouraging students to ask questions along the way. -
4.Modify Existing Activities
Many of the existing classroom projects and activities may already closely align with experiential learning practices. Review those activities that are practical and have original applications to identify which projects would best work with this learning approach. Take students through the Experiential Learning Model when completing this activity, leveraging guiding questions at each step to help trigger engagement and critical thinking. -
5.Practice Reflection
Reflection is an essential component of experiential learning, but it is an often overlooked skill for students. Take time to teach what good reflection looks like and continually incorporate it as a practice. You may benefit from creating a reflection journal for your students to work on during and after they complete a STEM project. -
6.Leverage Project-based Learning
Students can learn by doing—and they can also learn by teaching. Consider opportunities for students to conduct their own research on a STEM topic, potentially in collaboration with other students, and then present those to the class. Incorporate guiding questions and reflection into those presentations and projects.
Conclusion
Experiential learning has emerged as a powerful tool to bridge the gap between theoretical education and practical application, particularly in STEM fields. By immersing students in real-world scenarios, it builds a deeper connection to the subject matter, enhances critical thinking, and cultivates essential skills for future academic and professional success. Whether through hands-on projects, collaborative activities, or practical applications, this approach transforms the learning process into an engaging and impactful journey. Embracing experiential learning not only enriches education but also equips students with the confidence and adaptability needed to thrive in an ever-evolving world.




