Innovating Higher Education: Transitioning to Skills-Based Learning
August 13, 2024In today's rapidly evolving job market, practical skills have become more valuable than traditional degrees. Employers are increasingly hiring based on demonstrated competencies, with a growing number of students eager to pursue skills-based learning opportunities to advance their careers. As technology advances, the demand for new skills is escalating, necessitating continual learning, upskilling, and reskilling to thrive in the workforce.
Despite this demand, higher education institutions are struggling to keep pace. There is an urgent need for educational programs to focus more on imparting practical, in-demand skills. Students are increasingly seeking educational experiences that offer tangible outcomes and better prepare them for the workforce. Certificates and short-term courses, particularly those available online, are becoming popular for their efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and focus on essential skills.
Skills-based learning is also crucial for organizations facing challenges in bridging the skills gap. This targeted training ensures employees develop the specific abilities needed to excel in their roles, contributing significantly to organizational success. To remain relevant and effective, higher education must adopt skills-based approaches, helping students and professionals master the competencies required in the 21st century, and preparing them to meet the challenges of a dynamic job market.
How is Skills-based Learning defined?
Skills-based learning, also known as competency-based learning, focuses on developing practical abilities directly applicable to the workplace. Unlike traditional education that emphasizes theoretical knowledge, skills-based learning targets specific competencies essential for professional success. This approach addresses skill gaps and enhances performance by recognizing and honing individual strengths and needs, creating a personalized learning experience.
This targeted method contrasts with conventional "one-size-fits-all" training, as it customizes learning pathways to the unique requirements of each learner. Through hands-on projects, simulations, and real-world scenarios, learners gain practical experience, which not only boosts engagement but also improves job performance and satisfaction. The adaptability of skills-based learning makes it suitable across various industries, from healthcare to technology, ensuring that learners acquire relevant skills directly applicable to their careers.
Skills-based learning also builds a culture of continuous improvement. By focusing on practical application, learners refine and enhance their abilities through ongoing practice and feedback. This iterative process cultivates lifelong learning and professional development, making it an essential approach for staying competitive in a rapidly evolving job market. As the demand for specific skills increases with technological advancements, skills-based learning equips individuals with the tools needed to succeed, ensuring a resilient and capable workforce.
Benefits and Challenges of Skills-Based Learning
Skill-based learning has become increasingly vital in modern workplaces due to its direct applicability and focus on developing practical competencies. Here are some key benefits:
-
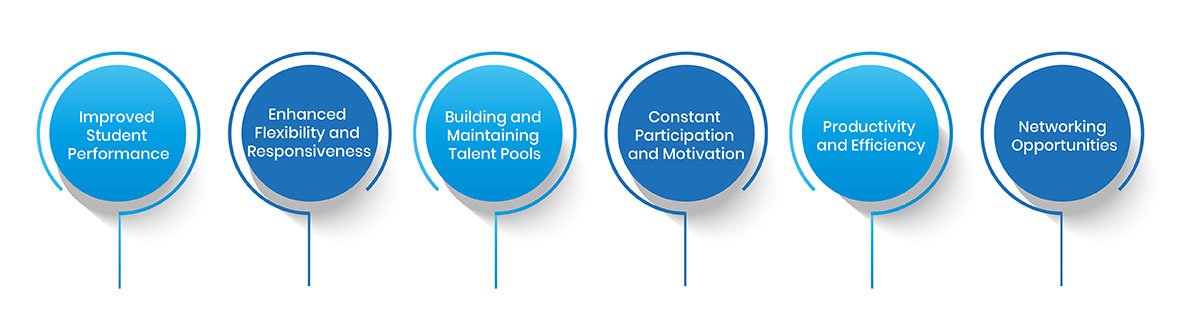
1. Improved Student Performance
Skill-based learning equips students with specific abilities for future careers, leading to better academic performance. This targeted training boosts confidence and autonomy, resulting in higher grades and successful projects. Aligning learning with real-world responsibilities ensures students are efficient and capable. -
2. Enhanced Flexibility and Responsiveness
As the job market evolves, students must adapt and learn new skills. Skill-based learning prepares them to handle changes effectively, whether in technology, industry trends, or career opportunities. -
3. Building and Maintaining Talent Pools
These programs keep students engaged and reduce dropout rates, preserving academic integrity. Professional development opportunities are crucial for retaining students seeking relevant and practical education. -
4. Constant Participation and Motivation
It involves interactive, hands-on experiences, making the learning process engaging and motivating. Students are more invested in training that directly impacts their future careers, leading to deeper learning and better knowledge retention. -
5. Productivity and Efficiency
Focusing on relevant skills helps educational institutions optimize teaching efforts, ensuring students acquire necessary skills efficiently. This leads to improved productivity and performance across the board. -
6. Networking Opportunities
It provides opportunities for students to connect with peers, mentors, and industry experts, leading to valuable collaborations and knowledge-sharing that enhance professional growth and development.
While the benefits are outstanding, it is important to consider few challenges as well.

-
1. Identifying Learning Gaps
Solution: Utilize a learning gap analysis framework to identify discrepancies between current abilities and desired competencies.
Understanding current student skills and the competencies needed for academic success is essential. This requires thorough assessments and performance reviews. -
2. Designing Relevant Learning Content
Solution: Involve subject matter experts in curriculum development to ensure learning is practical and relevant.
Generic educational programs often don’t meet specific needs. Customized learning content is crucial. -
3. Recognition and Standardization
Solution: Participate in educational initiatives to establish standardized certification frameworks.
Lack of standardized frameworks for skill validation can limit students' mobility and recognition in academic and career pathways. -
4. Resource Constraints
Solution: Use technology to deliver training and seek partnerships to provide necessary resources and expertise.
Skills-based learning requires substantial resources, which can be scarce, especially in underfunded areas. -
5. Tracking and Assessment
Solution: Use learning management systems and assessment tools to monitor progress and provide feedback.
Accurately tracking progress in SBL can be challenging.
The Gradual Shift to Skills-Based Learning
Despite the clear need for skills-based curricula, higher education faces significant challenges in its implementation. Still, the focus remains on traditional methods that prioritize theory, standardized testing, and rote learning over practical application and project-based learning. This disconnect is exacerbated by faculty designing courses based on theoretical knowledge rather than current industry demands. Engaging industry practitioners as educators can bridge this gap, yet comprehensive curriculum changes require extensive buy-in from various stakeholders, including administration, faculty, accreditors, and employers.
To effectively integrate skills-based learning, higher education must prioritize collaboration and innovation. Establishing partnerships with employers and certification providers offers critical insights into evolving skill requirements. Mapping these skills to program outcomes ensures graduates are equipped for the workforce. Continuous assessment of these programs is essential to maintain relevance and efficacy.
Embracing a growth mindset is vital for higher education to meet the demands of the future job market. Institutions must focus on continuous skills development and create agile programs to support lifelong learners in a rapidly changing workplace. Failure to adapt risks producing graduates unprepared for modern job requirements and widening the existing skills gap.
Implementing Skill-Based Learning in Educational Institutions
The right implementation of skill-based learning prepares students with practical skills bringing real-world success.
Let’s take a closer look:
-
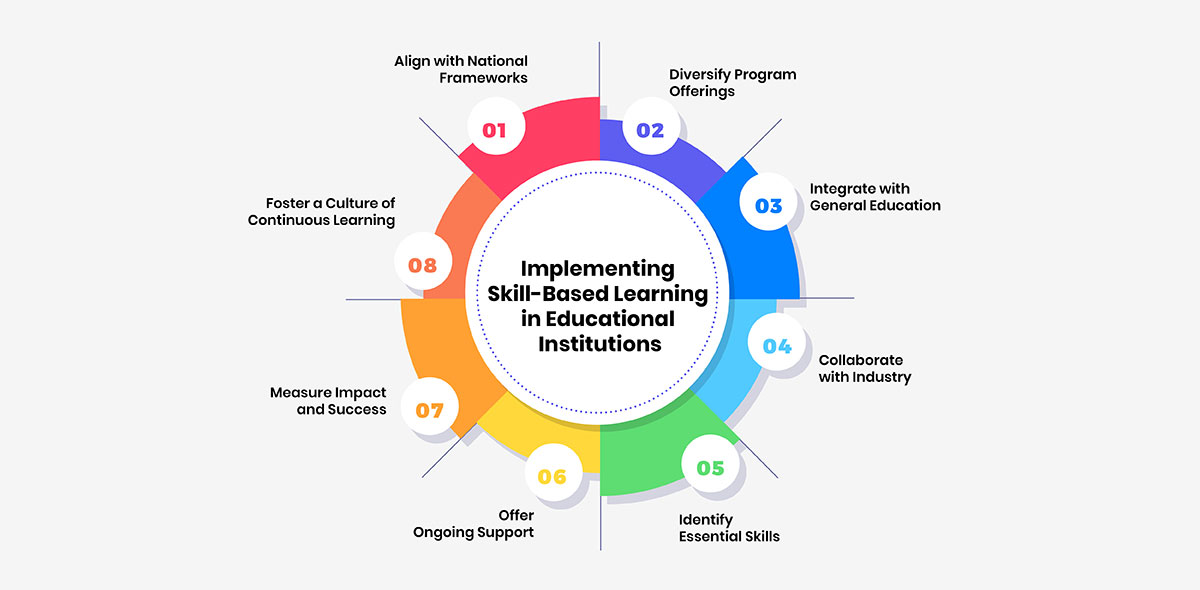
1. Align with National Frameworks:
Initiate by aligning educational programs with national skill qualification frameworks. This alignment ensures that curricula are industry-relevant and flexible, meeting both educational and market needs. -
2. Diversify Program Offerings:
Develop a range of skill-based programs at various levels—certificates, diplomas, and advanced degrees. This approach facilitates both vertical and horizontal mobility, allowing students to advance their education or career opportunities seamlessly. -
3. Integrate with General Education:
Ensure that skill-based learning integrates smoothly with traditional academic tracks. This integration supports a well-rounded education, blending practical skills with theoretical knowledge for a comprehensive learning experience. -
4. Collaborate with Industry:
Establish partnerships with industry leaders to keep curricula aligned with market demands. These collaborations provide real-world insights, ensuring that educational programs remain relevant and effective. -
5. Identify Essential Skills:
Identify the critical skills needed within specific educational or vocational pathways. Consulting industry experts and analyzing future trends can help in defining these competencies. -
6. Offer Ongoing Support:
Provide continuous support and resources to students. This includes access to learning materials, mentorship programs, and opportunities for applying new skills in real-world contexts. -
7. Measure Impact and Success:
Establish metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of skill-based learning programs. Regularly assess improvements in student performance, engagement levels, and skill acquisition to refine and enhance educational strategies. -
8. Foster a Culture of Continuous Learning:
Create an environment that promotes ongoing learning. Encourage leadership support, provide incentives for participation, and integrate learning opportunities into the regular educational framework.
The Future of Skill-Based Learning in Professional Development
Increased focus on upskilling and reskilling students to better prepare them for the demands of the modern workforce is necessary. Several trends will shape this future of skill-based learning in education:
-
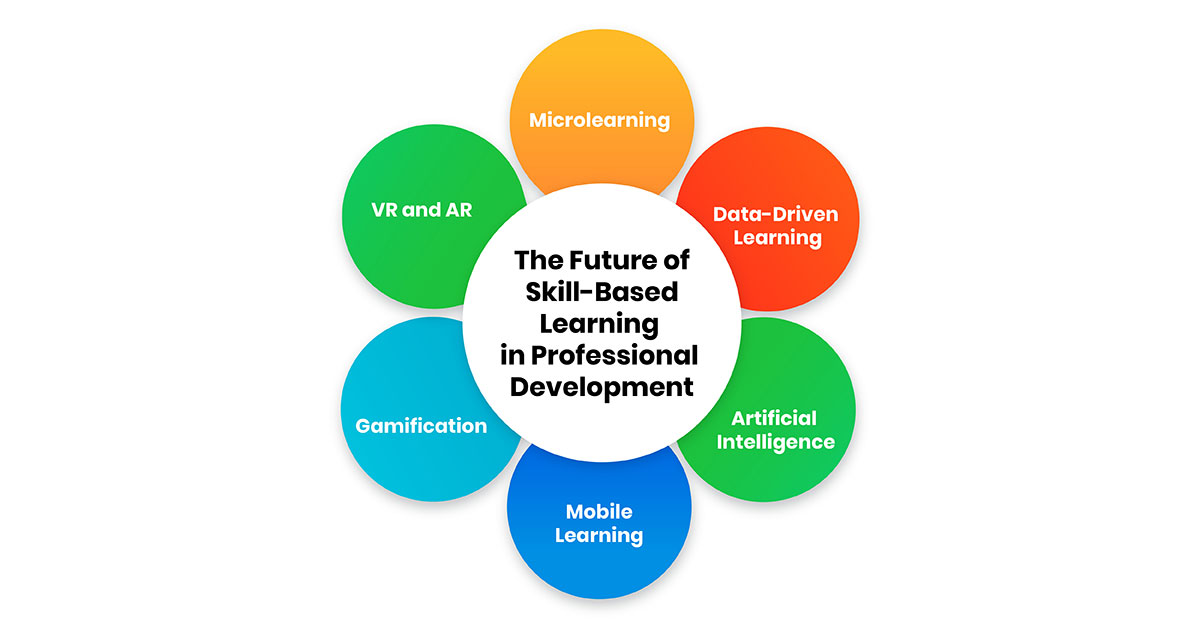
1. Microlearning:
Short, focused learning modules is becoming prevalent, allowing students to absorb information in manageable, actionable doses that fit seamlessly into their busy schedules. -
2. Data-Driven Learning:
Personalized learning experiences will be driven by data analytics, providing insights into individual learning patterns and targeting specific skill development needs. -
3. Artificial Intelligence:
AI is enhancing learning through virtual assistants and chatbots, offering personalized recommendations, answering questions, and providing on-demand assistance. -
4. Mobile Learning:
The rise of mobile devices is making learning more accessible through mobile apps, enabling students to engage with educational materials anytime, anywhere. -
5. Gamification:
Incorporating game elements such as points, badges, and leaderboards into learning modules will boost engagement and motivation, making skill acquisition more enjoyable and interactive. -
6. VR and AR:
Virtual and augmented reality technologies will transform education by offering immersive, hands-on experiences. VR simulations provide safe environments for practicing real-life scenarios, while AR offers interactive, real-time guidance and instructions.
Preparing students for the future requires more than just access to learning materials. Personalized guidance and mentorship are crucial for maximizing learning outcomes. Mentorship programs provide one-on-one support, boosting confidence, accelerating skill acquisition, and fostering career development.
Conclusion
Emphasizing continuous learning, leveraging innovative technologies, and fostering industry collaborations will ensure that both students and professionals are prepared for dynamic and successful careers. This shift not only enhances individual career prospects but also contributes significantly to bridging the skills gap in the workforce.




