The Need for Competency-Based Learning in Higher Education Institutions
December 17, 2024Educational institutions are increasingly adopting innovative approaches to enhance the learning experience, with competency-based learning (CBL) leading the way. This method allows students to progress at their own pace, focusing on mastering specific skills and knowledge made to prioritize individual needs. Competency Based Learning emphasizes outcomes, ensuring that students not only learn but also apply what they have learned effectively.
The Concept of Competency-Based Learning
The competency-based learning (CBL) model is a student-centered approach that prioritizes acquiring expertise in specific skills and knowledge over traditional time-bound educational methods. Unlike conventional systems, which focus on classroom hours and standardized progression, CBL allows students to advance at their own pace, ensuring they are proficient before moving forward. This flexibility empowers learners to change their educational journey to their individual needs and capabilities, making learning more effective and meaningful.
CBL emphasizes personalized progression, where students take control of their learning process. By focusing on competencies rather than rigid schedules, this approach equips students with practical skills that are directly relevant to their future career and life challenges. Institutions adopting CBL often witness better engagement and improved outcomes as students are motivated by the ability to progress based on their demonstrated proficiency. Its focus on purposeful and adaptable learning is making CBL a cornerstone of modern education.
Core Principles of Competency-Based Learning
Competency-based learning (CBL) revolves around a student-centered framework that prioritizes skill grasping, personalized education, and real-world relevance. Here are the key principles that define this approach:
-
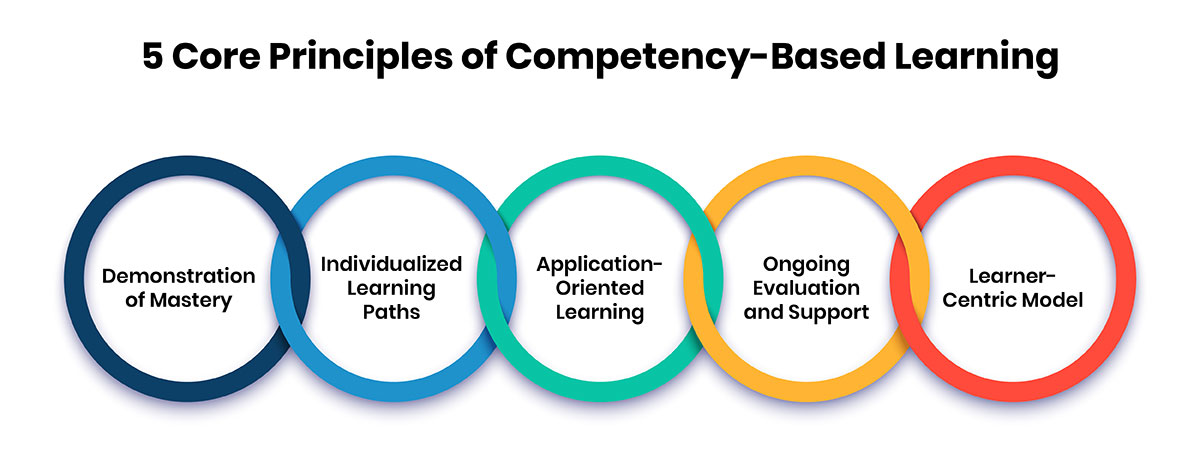
1. Demonstration of Mastery
Students progress only when they can clearly demonstrate mastery of the required skills or knowledge. This ensures a deep and thorough understanding of each competency rather than moving forward based on classroom hours or predetermined timelines. -
2. Individualized Learning Paths
CBL allows for a highly personalized educational journey customized to each learner’s pace, style, and specific needs. This customization helps create an effective and engaging learning environment where every student can thrive. -
3. Application-Oriented Learning
The focus on practical, real-world skills ensures that learners acquire knowledge they can immediately apply in relevant contexts. This makes the learning process more meaningful and prepares students for real-life challenges. -
4. Ongoing Evaluation and Support
Students are assessed continuously through diverse methods, allowing for a more comprehensive evaluation of their abilities. Regular feedback helps them identify areas of improvement and track their progress toward mastery. -
5. Learner-Centric Model
Placing the student at the heart of the process, CBL fosters active involvement, self-direction, and accountability. This approach encourages learners to take ownership of their education, resulting in a more empowering and fulfilling experience.
Key Benefits of the Competency-Based Learning Approach
Competency-Based Learning (CBL) is revolutionizing education, and this approach offers numerous benefits that enhance the learning experience for students while aligning with the evolving demands of modern education and the job market.
-
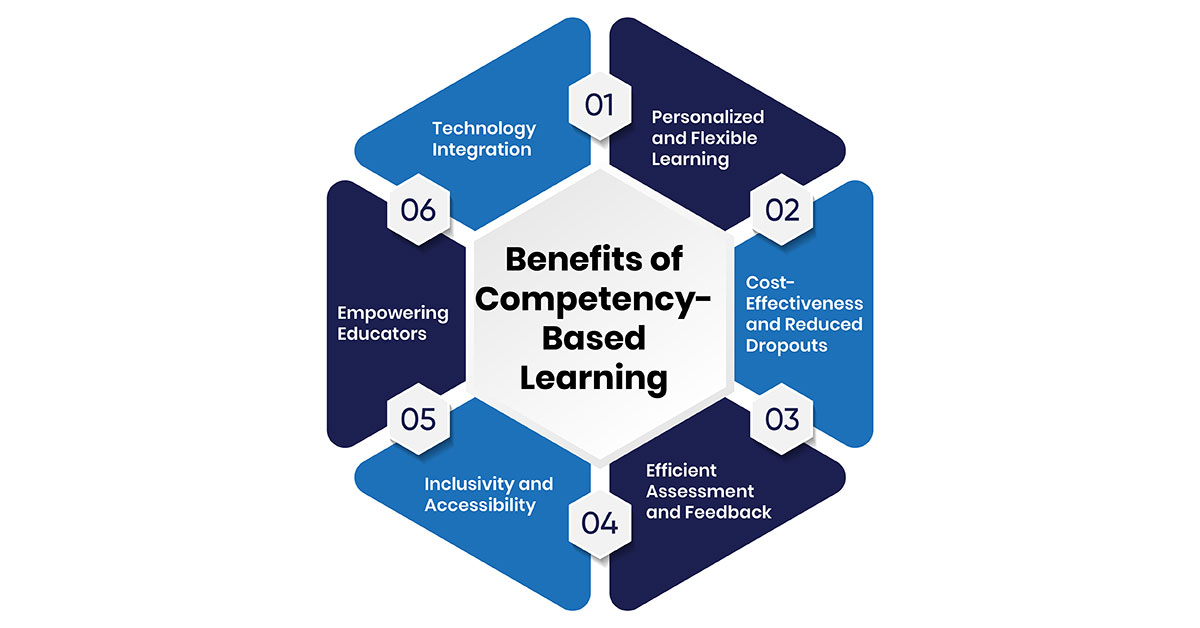
1. Personalized and Flexible Learning
A significant advantage of CBL is its ability to adapt to individual learning needs. Students can progress at their own pace, dedicating more time to challenging areas while moving quickly through topics they already understand. This flexibility ensures that students gain a strong command of essential skills before advancing, leading to better outcomes. -
2. Cost-Effectiveness and Reduced Dropouts
CBL programs are often more cost-efficient than traditional classroom-based systems. Online delivery reduces operational expenses, making courses more affordable. Moreover, by allowing students to progress at their own pace and take assessments when ready, CBL significantly lowers dropout rates, ensuring more students successfully complete their education. -
3. Efficient Assessment and Feedback
Continuous assessments in CBL provide regular insights into student progress. This system allows teachers to offer timely feedback, helping learners identify strengths and areas for improvement. It also enables educators to improvise their teaching strategies to meet the unique needs of each student, enhancing overall effectiveness. -
4. Inclusivity and Accessibility
CBL promotes inclusivity by accommodating diverse learning preferences and needs. Its flexible nature allows students with disabilities or those requiring special accommodations to participate fully. Online CBL programs also eliminate geographical barriers, ensuring that learners can access quality education from anywhere. -
5. Empowering Educators
Teachers play a critical role in CBL, shifting from traditional lecturing to roles as mentors and coaches. This dynamic enables educators to focus on personalized guidance, professional development, and improving student outcomes. -
6. Technology Integration
Adaptive learning platforms, online resources, and learning management systems (LMS) allow institutions to track individual progress while offering the flexibility to move at a pace suited to each student’s needs. By utilizing these digital platforms, institutions can also collect data on student progress, engagement, and achievement. This data can be used to identify trends and intervene early when students are struggling.
Best Practices for Implementing Competency-Based Education
To implement a competency-based education (CBE) program effectively, it’s important to follow a comprehensive and phased approach that aligns with both the needs of students and the institutional context.
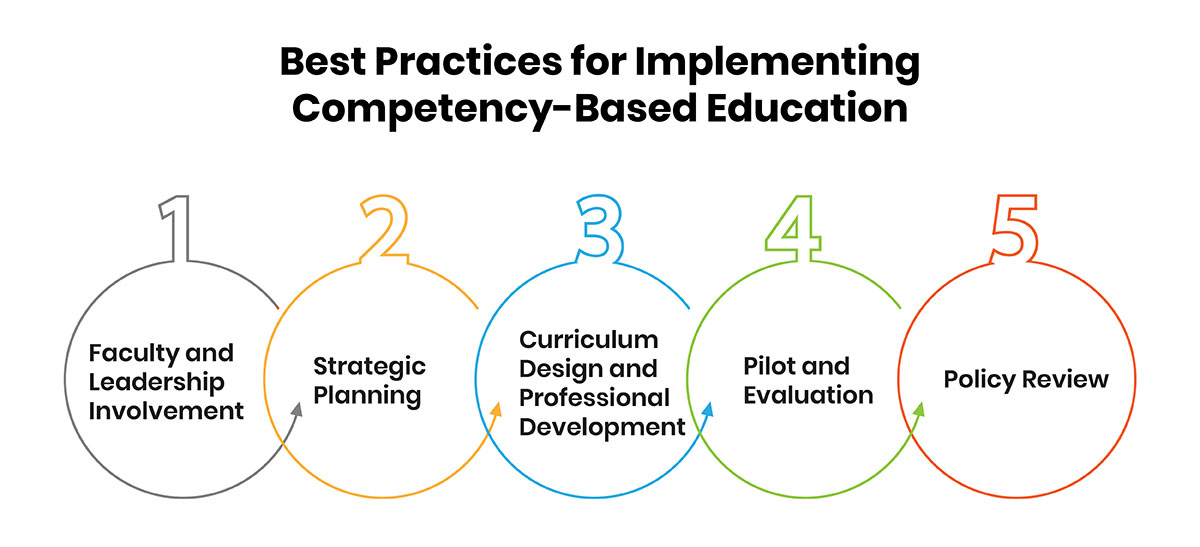
- 1. Faculty and Leadership Involvement: Engaging faculty in the design and execution of the CBE program is crucial, as they ensure its academic integrity and fit within the institution's mission. Institutional leadership also plays a pivotal role by advocating for the program, ensuring proper buy-in, and guiding the change management process.
- 2. Strategic Planning: Careful strategic planning is essential, including realistic student demand, resource allocation, and clear success metrics. This includes determining how the program will be phased in, balancing growth with institutional capacity.
- 3. Curriculum Design and Professional Development: Aligning the curriculum with competency standards and developing clear learning objectives is essential. Teachers should be supported with professional development to understand and implement Competency-Based Education strategies effectively.
- 4. Pilot and Evaluation: A smaller pilot phase allows schools to gather feedback, assess student performance, and refine the program before full implementation.
- 5. Policy Review: Shifting from a credit-hour model to a competency-based approach requires reviewing and possibly revising institutional policies, including those related to admissions, financial aid, and academic advising.
Transformative Impacts of Competency-Based Learning on Students
Competency-Based Learning impacts students by prioritizing learner-driven progress and flexible educational paths. Here are key points that highlight its impact:
-
Becomes a Master
CBL ensures that students progress based on their ability to demonstrate mastery of specific competencies, rather than time spent in class. This approach ensures no gaps in learning, as students only move on when they are fully confident in their skills. -
Maturing into autonomy
By giving students control over their learning pace, CBL builds greater ownership of their education. Students become more engaged and motivated when they can learn at their own speed without external pressures to keep up with a set timeline. -
Receives appropriate support
CBL offers timely, ongoing support from educators, allowing students to receive assistance precisely when they need it. With assessments designed to focus on mastery and practical skills, students get more accurate feedback on their abilities, helping them improve continuously. -
Development of Soft Skills
In addition to academic skills, CBL helps students develop essential soft skills, such as critical thinking, communication, collaboration, and problem-solving. These skills are vital for adapting to diverse and evolving workplaces. -
Emerging as Practical and Workforce-Ready
CBL emphasizes real-world applications, preparing students with relevant skills for their careers. By aligning educational goals with workplace demands, this approach equips learners to meet employer expectations in a competitive job market. Digital badging further enhances this readiness by providing tangible proof of competencies that students can showcase to potential employers. -
Lifelong Learning and Growth
CBL fosters a culture of continuous improvement by emphasizing the importance of effort and learning from mistakes. This growth mindset prepares students for lifelong learning in a world where adaptability and skill development are essential for success.
Conclusion
Competency-Based Learning (CBL) represents a dynamic shift in education that centers on the acquisition and application of specific skills, ensuring students progress according to their abilities rather than time spent in class. CBL’s adaptability and emphasis on continuous support ensure that students are not only academically proficient but also workforce-ready, equipped with the competencies required for success in today’s dynamic professional environments. As educational institutions continue to evolve, embracing CBL will be essential for preparing students to thrive in an ever-changing world.




